Threat Modeling - Part 3
What will we learn?
- Well….STRIDE!
STRIDE
Microsoft developed this methodology in the early 2000s. This methodology shows that nearly all the threats you can think of will fall under one or more of these
Spoofing: Pretending to be someone else, like stealing a password to log in as another user.
Tampering: Changing or altering data, such as modifying files or messages in transit.
Repudiation: Denying actions, like a user claiming they didn’t send a message because there’s no proof.
Information Disclosure: Leaking sensitive information, such as exposing personal data or private files.
Denial of Service (DoS): Overloading a system so it can’t function properly, like flooding a website with traffic or overwhelming a service to affect availability.
Elevation of Privilege: Gaining more access than you’re supposed to, such as a regular user becoming an administrator.
STRIDE helps teams think through these threats and design safeguards to improve security.
Spoofing
Imitating or Masquerading the real user / process / etc. The main idea is to defeat Authentication.
Spoofing Client - External Entity
Spoofing Data Flows
Spoofing Processes
Tampering
Integrity driven attack. Modify an entity/object without authorization affecting the Integrity aspect.
Tampering with a Process
Tampering with a Data Flow
Tampering with a Data Store
Ex → SQL injection and change data in the data store.
Repudiation
Attacks against Non-Repudiation. Negating accountability against all our actions….think wiping logs. Typically a secondary threat after an initial attack.
Repudiation against a process → Attacker gains access to admin interface and disables logging.
Repudiation against a data store → Attacker gains access to logs and deletes the logs.
Information Disclosure
Confidentiality breaching attack. Typically attacks against Authorization.
ID - Process → Think IDORs
ID - Data Store → Think network sniffers
ID - Data Flow → Found an encryption key on a system and use it to decrypt data stores
Denial of Service
Attack against Availability. Typically network focused attack but also against data flow/process and more.
DoS - Service Process → Think overloading an input and corresponding service to overwork the CPU eventually crippling the service.
DoS - Data Store → Drop table during a SQLi attack
DoS - Network → Exhaust network resources and cause downtime
Elevation of Privilege
Done against processes. Use a lower privileged user to vertically or horizontally increase privileges to increase the scope of the attack and gain higher privileges.
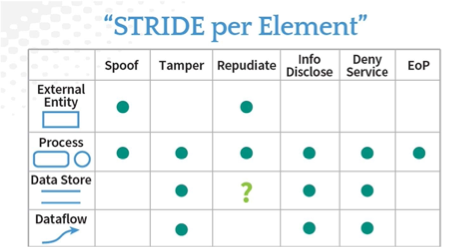
Speed up your Threat Modeling
This handy little chart from Adam Shostack talks about the typical threat categories based on the element in question.
Example
Example: Simple Threat Model
System: User uploads data to a file server.
Let’s put on our STRIDE hats and start documenting all the threats that come to mind based on what we understood earlier.
| Threat Scenario | STRIDE Categories | Severity |
| Upload Malware to File server | E, D | Critical |
| Upload a Shell to File Server and gain persistent access | E, ID | Critical |
| Upload a huge file and trigger DoS | D | High |
| Overwhelm Application with multiple file uploads at the same time, triggering DoS | D | High |
| Based on save operation, attacker could trigger command injection on upload, to delete files or content on the server | D, E | Critical |
| Intercept the uploaded data / Network Sniffing to steal data | I | High |
That’s all folks! See you in the next one.